 Visual Paradigm Desktop |
Visual Paradigm Desktop |  Visual Paradigm Online
Visual Paradigm OnlineThis case study delves into the practical application of a mind map generated by Visual Paradigm AI, titled “Healthy Meal Prep Ideas.” The mind map serves as a visual framework for organizing nutritious meal components, preparation strategies, and sample recipes. Created to assist individuals in adopting sustainable healthy eating habits, it structures ideas around a central theme with branching categories. The purpose of this case study is to explore the key concepts embedded in the mind map, illustrate them with examples, and demonstrate their real-world implementation through a hypothetical scenario. By analyzing this mind map, we highlight how such tools can simplify meal planning, promote balanced nutrition, and support long-term wellness goals.
The mind map’s structure follows a node-tree format, with the root node “Healthy Meal Prep Ideas” branching into six main categories: Protein Options, Vegetable Choices, Grain Options, Healthy Fats, Meal Prep Tips, and Sample Meal Ideas. Each category includes sub-nodes that provide specific, actionable suggestions. This hierarchical design makes it easy to navigate and expand upon, turning abstract health advice into tangible plans.
Meal prepping has gained popularity as a strategy to combat the challenges of busy lifestyles, poor dietary choices, and time constraints. According to ongoing health trends as of 2026, consistent meal preparation correlates with better weight management, reduced food waste, and improved nutrient intake. The Visual Paradigm AI mind map addresses these by categorizing essential elements of healthy meals, drawing from evidence-based nutritional principles such as the importance of macronutrient balance (proteins, carbs, fats) and micronutrient diversity (from vegetables and whole foods).

The mind map was authored by “MindMap Assistant” (version 1.0) and emphasizes variety, simplicity, and sustainability. It avoids overly restrictive diets, instead focusing on inclusive options like plant-based alternatives, making it adaptable for diverse dietary needs, including vegetarian, gluten-free, or high-protein preferences.
The mind map’s strength lies in its breakdown of meal prep into core components. Below, we examine each main branch, explaining the key concepts and providing practical examples to illustrate their application.
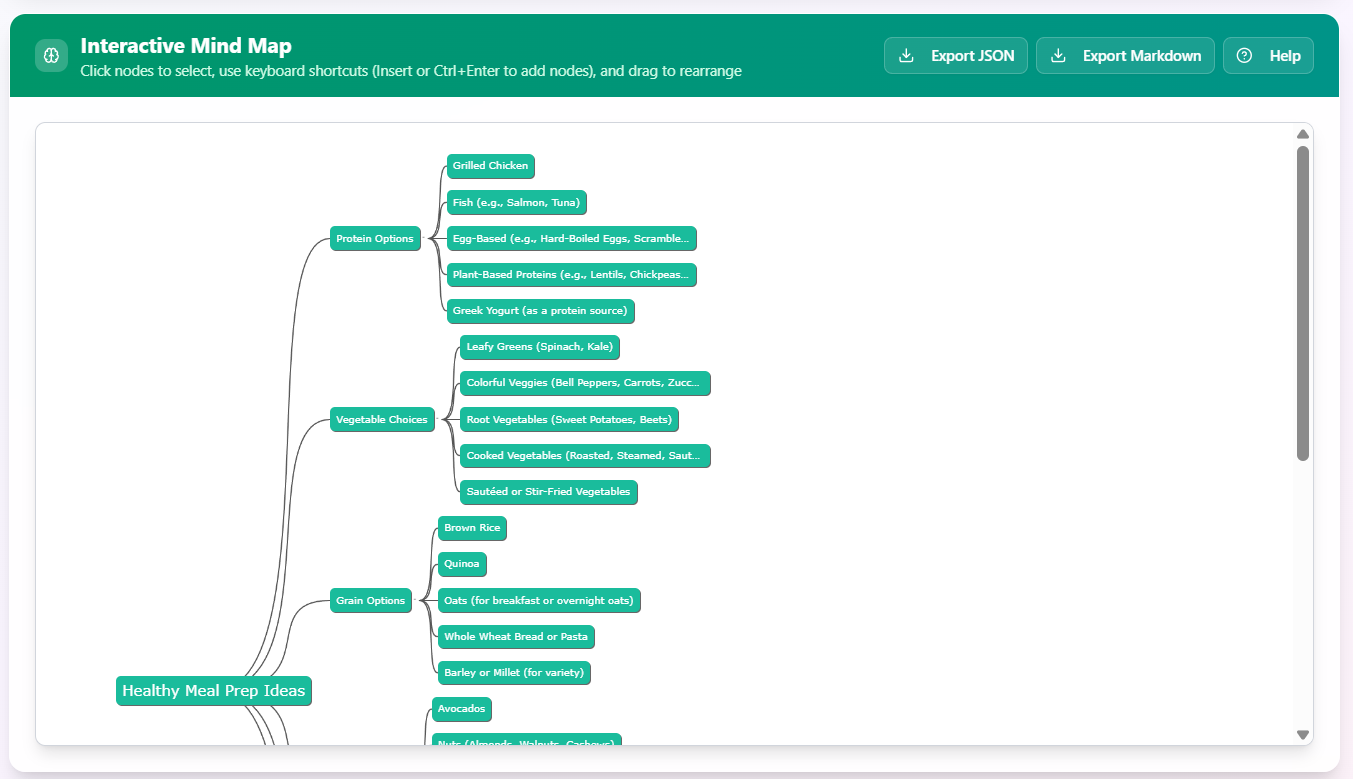
Proteins are fundamental for muscle repair, satiety, and overall energy. The mind map emphasizes diverse sources to cater to different tastes and dietary restrictions, ensuring meals remain interesting and nutritionally complete.
Grilled Chicken: A lean, versatile protein that’s easy to season and portion. Example: Marinate chicken breasts in herbs and lemon, grill in batches, and store for salads or wraps.
Fish (e.g., Salmon, Tuna): Rich in omega-3 fatty acids for heart health. Example: Bake salmon fillets with minimal oil for a quick prep that reheats well without drying out.
Egg-Based (e.g., Hard-Boiled Eggs, Scrambled Eggs): Affordable and quick-cooking options for breakfast or snacks. Example: Boil a dozen eggs at once for easy addition to veggie bowls or as standalone protein boosts.
Plant-Based Proteins (e.g., Lentils, Chickpeas, Tofu): Ideal for vegans or those reducing meat intake, providing fiber alongside protein. Example: Cook lentils in a slow cooker with spices for a base in soups or stews.
Greek Yogurt (as a protein source): High in probiotics and calcium, suitable for sweet or savory dishes. Example: Use plain Greek yogurt as a base for dips or parfaits, layered with fruits for a post-workout snack.
Vegetables supply vitamins, minerals, and fiber, forming the bulk of healthy meals to promote digestion and disease prevention. The mind map advocates for color variety and cooking methods to maximize appeal and nutrient retention.
Leafy Greens (Spinach, Kale): Nutrient powerhouses with iron and antioxidants. Example: Wash and chop kale for massaged salads that store well without wilting.
Colorful Veggies (Bell Peppers, Carrots, Zucchini): Add vibrancy and beta-carotene. Example: Slice bell peppers and carrots into sticks for raw snacking or roasting.
Root Vegetables (Sweet Potatoes, Beets): Starchy options for sustained energy. Example: Dice and roast sweet potatoes with herbs for a side that pairs with any protein.
Cooked Vegetables (Roasted, Steamed, Sauteed): Enhances flavor and digestibility. Example: Steam broccoli florets in bulk for easy reheating in stir-fries.
Sautéed or Stir-Fried Vegetables: Quick methods to retain crunch. Example: Stir-fry zucchini with garlic in a wok for a flavorful addition to grain bowls.
Whole grains provide complex carbohydrates for energy and fiber for gut health. The mind map suggests alternatives to refined grains for better blood sugar control.
Brown Rice: A staple with more nutrients than white rice. Example: Cook a large pot and portion into containers for base layers in meals.
Quinoa: A pseudo-grain that’s a complete protein. Example: Rinse and boil quinoa, then fluff for use in salads or as a rice substitute.
Oats (for breakfast or overnight oats): Versatile for sweet preparations. Example: Mix oats with milk and fruits overnight for grab-and-go breakfasts.
Whole Wheat Bread or Pasta: Higher in fiber for fullness. Example: Prepare whole wheat pasta al dente and toss with veggies for cold salads.
Barley or Millet (for variety): Lesser-known grains to prevent monotony. Example: Simmer barley in broth for a chewy addition to soups.
Fats are essential for hormone production and nutrient absorption. The mind map focuses on unsaturated sources to support heart health without excess calories.
Avocados: Creamy texture for spreads or toppings. Example: Mash avocados for guacamole or slice for salads.
Nuts (Almonds, Walnuts, Cashews): Portable snacks with healthy oils. Example: Portion nuts into small bags to avoid overeating.
Seeds (Chia, Flax, Sunflower): Easy to sprinkle for omega-3 boosts. Example: Add chia seeds to yogurt or smoothies for thickness.
Olives or Olive Oil (as a dressing): Mediterranean staples for flavor. Example: Whisk olive oil with vinegar for a simple vinaigrette.
Nut Butters (Peanut, Almond): Spreadable for sandwiches or dips. Example: Spread almond butter on apple slices for a balanced snack.
These practical strategies ensure efficiency and food safety, turning concepts into habits.
Prep in Bulk and Freeze Portions: Saves time long-term. Example: Cook extra chicken and freeze in single servings for up to three months.
Use Airtight Containers for Storage: Prevents spoilage. Example: Invest in glass containers to store prepped veggies without absorbing odors.
Batch Cook and Store in Portions: Facilitates portion control. Example: Divide cooked quinoa into daily servings to avoid overeating.
Keep Recipes Simple and Balanced: Reduces overwhelm. Example: Aim for one protein, two veggies, and one grain per meal.
Include a Variety of Colors and Nutrients: Ensures comprehensive nutrition. Example: Rotate veggies weekly to cover different vitamins.
The mind map culminates in integrated examples that combine the above concepts, demonstrating balanced, prep-friendly meals.
Grilled Chicken & Veggie Bowls with Quinoa: A protein-packed lunch featuring grilled chicken over quinoa, topped with colorful veggies like bell peppers and zucchini, drizzled with olive oil.
Salmon with Roasted Vegetables and Brown Rice: Omega-rich salmon served with roasted root veggies like sweet potatoes and brown rice for a satisfying dinner.
Chickpea Salad with Mixed Greens and Olive Oil Dressing: A plant-based option with chickpeas, leafy greens like spinach, and a simple olive oil vinaigrette for lightness.
Tofu Stir-Fry with Brown Rice and Steamed Broccoli: Vegan stir-fried tofu with brown rice and steamed veggies, seasoned lightly for flavor without excess sodium.
Greek Yogurt Parfait with Berries and Granola: A sweet breakfast layering Greek yogurt with fresh berries, seeds, and homemade granola for crunch.
Consider Sarah, a 35-year-old office worker struggling with inconsistent eating habits. Using the mind map, she plans her weekly prep on Sundays. She selects grilled chicken and tofu as proteins, incorporates leafy greens and root vegetables, chooses quinoa and brown rice as grains, and adds avocados and nuts for fats. Following the tips, she batch-cooks and stores in airtight containers. For instance, she assembles five quinoa bowls with chicken, veggies, and olive oil dressing, freezing extras. Over the week, she rotates sample ideas like the chickpea salad for variety. After a month, Sarah reports increased energy, weight loss, and reduced takeout spending.
Benefits include time efficiency, cost savings, and nutritional balance, as the mind map encourages diversity. Challenges may involve initial planning time or ingredient availability, but these diminish with practice. Adaptations, like substituting seasonal veggies, enhance sustainability.
The Visual Paradigm AI mind map on “Healthy Meal Prep Ideas” offers a robust framework for transforming dietary intentions into action. By integrating key concepts like diverse proteins and practical tips with illustrative examples, it empowers users to achieve healthier lifestyles. This case study underscores the value of visual tools in health management, suggesting further expansions could include calorie estimates or shopping lists for even greater utility.
AI-Powered Visual Modeling and Design Solutions by Visual Paradigm: Explore cutting-edge AI-driven tools for visual modeling, diagramming, and software design, enabling faster, smarter development workflows.
Visual Paradigm – All-in-One Visual Development Platform: A comprehensive platform for visual modeling, software design, business process modeling, and AI-powered development tools.
AI Chatbot Feature – Intelligent Assistance for Visual Paradigm Users: Leverage AI-powered chatbot functionality to get instant guidance, automate tasks, and enhance productivity within Visual Paradigm.
Visual Paradigm Chat – AI-Powered Interactive Design Assistant: An interactive AI chat interface that helps users generate diagrams, write code, and solve design challenges in real time.
AI Textual Analysis – Transform Text into Visual Models Automatically: Use AI to analyze text documents and automatically generate diagrams such as UML, BPMN, and ERD for faster modeling and documentation.
Visual Paradigm AI Chatbot Enhances Multi-Language Support …: 7 hours ago · Discover the latest updates to Visual Paradigm ‘s AI -Powered visual modeling software, including multi-language UI and improved chat content localization. Experience seamless AI diagram generation in languages like Spanish, French, Chinese, and more with our AI chatbot for UML and other diagrams.
AI -Powered BI Analytics by Visual Paradigm – ArchiMetric: Get started in under a minute at ai . visual – paradigm .com/tool/ ai -powered-bi-analytics. No installation, no signup required for most features.
Discover the Power of Visual Paradigm ’s AI -Powered… – Visualize AI: While tools like Google’s AI Image Translator (via Google Lens and Google Translate) offer convenience, Visual Paradigm ’s AI -Powered Image Translator takes the lead with…
AI Chatbot for Diagramming: How It Works with Visual Paradigm: The Visual Paradigm AI chatbot is an AI -powered modeling assistant that turns natural language into diagrams. It doesn’t require users to learn specific modeling standards or syntax.
Free Online Class Diagram Tool – Create UML Class Diagrams Instantly: A free, web-based tool that enables users to create professional UML class diagrams quickly and easily without installation.
Complete UML Class Diagram Tutorial for Beginners and Experts: A step-by-step tutorial that walks users through creating and understanding UML class diagrams, ideal for learning software modeling.
What Is a Class Diagram? – A Beginner’s Guide to UML Modeling: An informative overview explaining the purpose, components, and importance of class diagrams in software development and system design.