 Visual Paradigm Desktop |
Visual Paradigm Desktop |  Visual Paradigm Online
Visual Paradigm OnlineImagine a user who wants to quickly understand how a peer-to-peer car sharing system works—without writing code or manually drawing every step.
They don’t need to start from scratch. With AI-powered modeling software, they can describe the system’s flow in plain language and get a clear, visual representation of how it functions.
This isn’t just about diagrams. It’s about understanding how requests travel, how responses are handled, and how different parts of the system react to real-world conditions.
The result? A clear, actionable sequence diagram that maps user actions, system responses, and edge cases—like no cars available or network issues—within minutes.
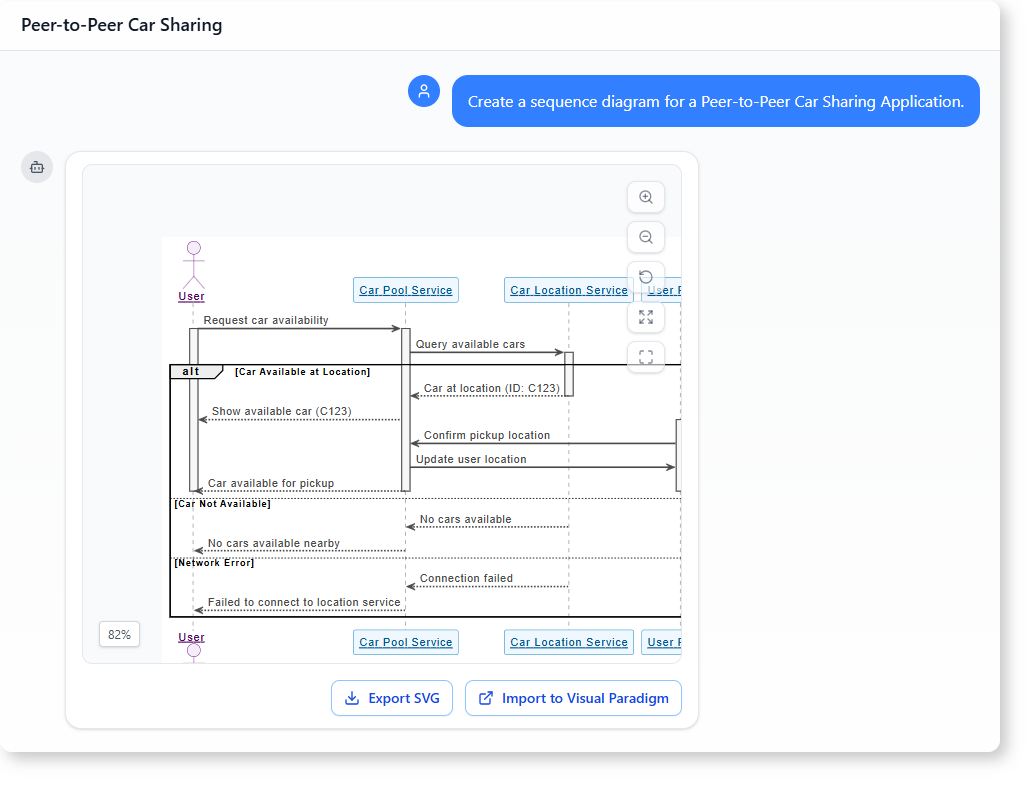
A peer-to-peer car sharing system depends on real-time interaction between users and services.
When a user wants to rent a car, the system must:
Without a clear visual of these interactions, the design can fall short.
That’s where a sequence diagram tool comes in.
It shows the exact flow of messages between participants—like a user, a car pool service, and a location service—making it easy to see what happens at each step.
The user started with a simple goal: build a sequence diagram for a peer-to-peer car sharing application.
They didn’t need to know PlantUML or any modeling syntax. They just said:
“Create a sequence diagram for a Peer-to-Peer Car Sharing Application.”
The AI-powered modeling software interpreted the request and generated a complete flow with participants, messages, and conditional branches.
Next, the user asked:
“Generate a summary of how the system handles requests and responses based on this sequence diagram.”
The tool didn’t just draw a diagram. It explained the logic behind it—how the system responds to different scenarios.
The output wasn’t just a diagram. It was a working system flow broken down into:
Each step includes message flow, timing, and participant roles. The diagram shows:
This level of clarity helps developers and product teams understand not just the flow—but the edge cases that can break the system.
This kind of modeling isn’t just for tech teams.
Business analysts can use it to see how a P2P car sharing system responds to user actions.
Product managers can validate user journeys.
And developers get a clear map of how messages move between services.
In this case, the AI generator for sequence diagram turned a simple prompt into a detailed, conditionally structured flow that mirrors real-world behavior.
The result is a document that’s easy to read, easy to explain, and easy to build upon.
| Feature | Traditional Modeling Tools | AI-Powered Modeling Software |
|——–|—————————|—————————–|
| Setup time | Hours to define participants and flows | Minutes with natural language prompts |
| Handling of edge cases | Requires manual configuration | Automatically detected and displayed |
| Real-time feedback | Limited | Immediate visual and textual summaries |
| User accessibility | Requires technical knowledge | Works with non-technical users |
This shows why AI-powered modeling software is a better fit for fast-moving, user-centered systems like P2P car sharing.
You don’t need to be a systems expert to understand how a system works.
With AI-powered modeling software, anyone can describe a use case—like a user looking for a car—and get back a professional-grade sequence diagram with clear message flow and response logic.
It’s not magic. It’s intelligence built into the tool.
And it works best when you describe the system naturally—without technical jargon.
Q: Can I use this tool to model a request-response flow diagram for any system?
A: Yes. Whether it’s a car sharing app, a ride-hailing platform, or a booking system, you can describe the interaction and get a clear sequence diagram that shows how requests travel and how responses are returned.
Q: Does this tool work with P2P car sharing system design?
A: Absolutely. The AI understands the logic behind peer-to-peer systems—like location checks, user confirmation, and error handling—and generates accurate diagrams that reflect real-world behavior.
Q: How does the AI know when to show conditional branches like ‘car not available’?
A: The tool interprets natural language prompts and identifies logical decisions. When the user talks about ‘checking availability’ or ‘handling errors,’ the AI recognizes these as decision points and builds them into the diagram with appropriate conditionals.
Q: Is this tool suitable for non-technical users?
A: Yes. You don’t need to know modeling syntax. Just describe the flow in plain English, and the AI-powered modeling software builds the diagram and provides a clear summary.
Ready to map out your system’s interactions? Give our AI-powered modeling software a try at Visual Paradigm’s AI Chatbot today!.